RootFS Build Implementation
This chapter explains the implementation of the RootFS build routine. According to the RootFS evaluation results, Ansible has been used for the implementation.
The implementation is available online in the RootFS build routine repository.
Steps
The necessary steps for the RootFS Build routine have already been specified in the corresponding evaluation chapter. As it can be seen there, the build steps are different for native and cross containers. Therefore, the RootFS build routine needs to be aware of the context.
Context Awareness
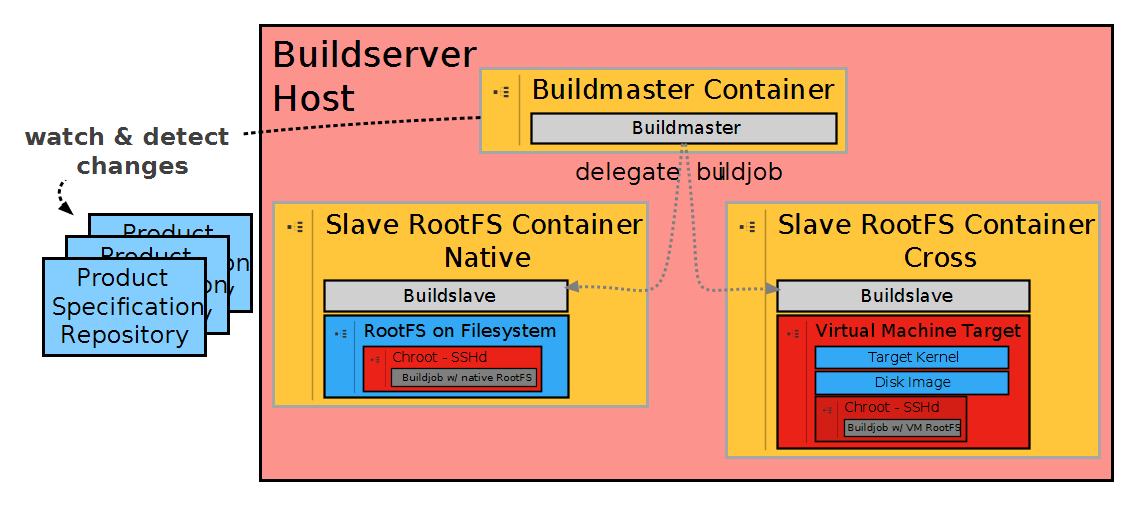
The RootFS build process is triggered for every change in the RootFS product specifications repository. Please have a look at the following picture, especially how the build delegation to the RootFS containers is visualized.
According to the design and evaluation results, the RootFS build routine can either be run in a RootFS container for the native or cross architecture.
Native/Cross RootFS Detection
Both scenarios must be handled differently. Environment variables are used to indicate the target architecture in the buildslave container. A comparison of the target architecture and the detected native architecture indicates whether the build routine must handle a native or cross target RootFS. The build routine involves setting up the build environment depending on whether it is a cross container or not.
Plays Overview
Altogether, the build routine consists of 10 plays. The following table gives a
brief overview about all the plays. The host column is directly taken from the
ansible-playbook --list-tasks commands, and gives some insight how the host
organization options have been used. The example shows the procedure for a fresh
build environment. Some of these steps are automatically skipped on subsequent
build jobs, e.g. play #3 and #6.
| Play # | Cross/Native | Host | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | both | localhost | Native/Cross detection and fact assignment |
| #2 | both | localhost | Download stage3; Prepare and mount the RootFS image; Unpack stage3; Sync portage tree |
| #3 | cross | localhost | Create dummy hosts group for cross targets |
| #4 | cross | localhost_cross | Download and unpack Qemu kernel files |
| #5 | cross | target_cross | Estimate the crossdev parameters |
| #6 | cross | localhost_cross | Build the cross-toolchain using crossdev; Setup distccd |
| #7 | both | localhost | Start the target system accordingly (Qemu or proot) |
| #8 | both | target | Copy Pre-Overlay; Run Pre-Install-Comands; Install Packages |
| #9 | both | target | Copy Post-Overlay; Run Post-Install-Comands |
| #10 | both | localhost | Pack the RootFS content and Portage Snapshots |
Notes
The actions that are marked bold process the configuration.yml and overlay directories that have been stored in the RootFS product specification repository. If you are interested in an example, please have a look at the RootFS Usage page.
The table has been simplified, since all plays consists of a total of 137 tasks. Please investigate the source code of the build routine if you are interested in more details.